Fossil Fuels - Tradition Facing Drastic Alterations
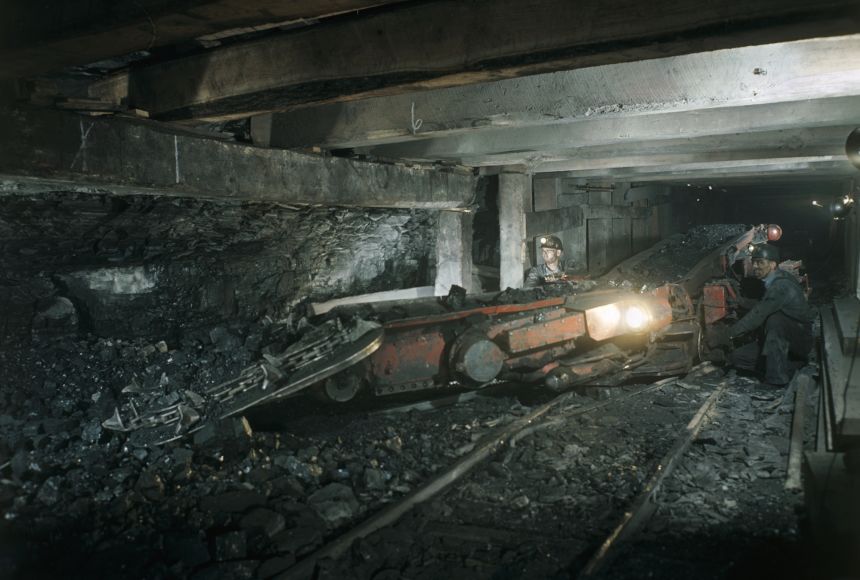
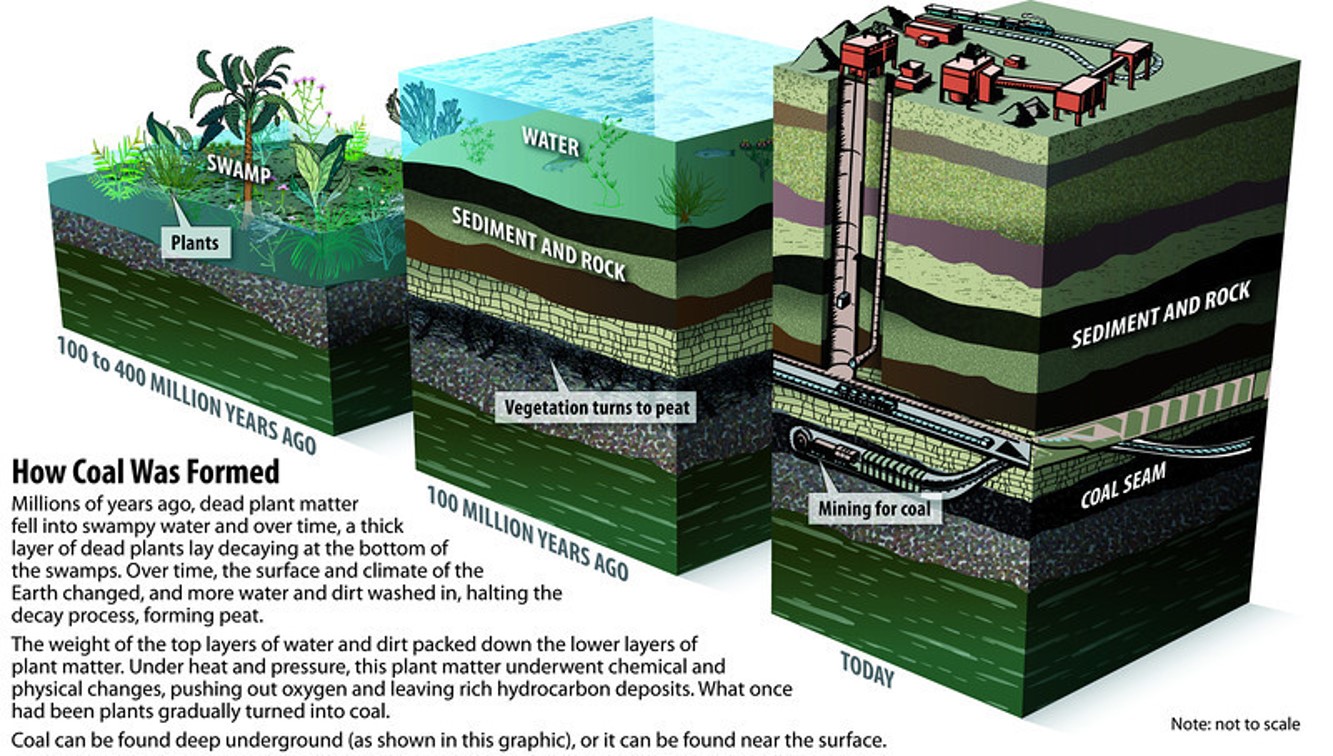
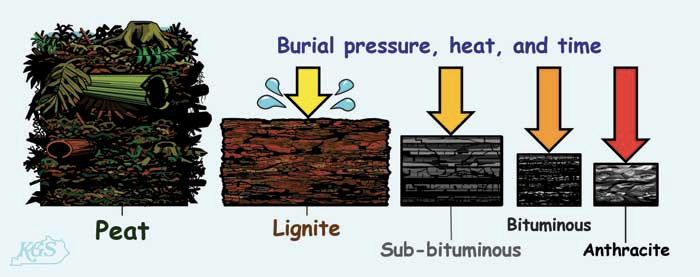
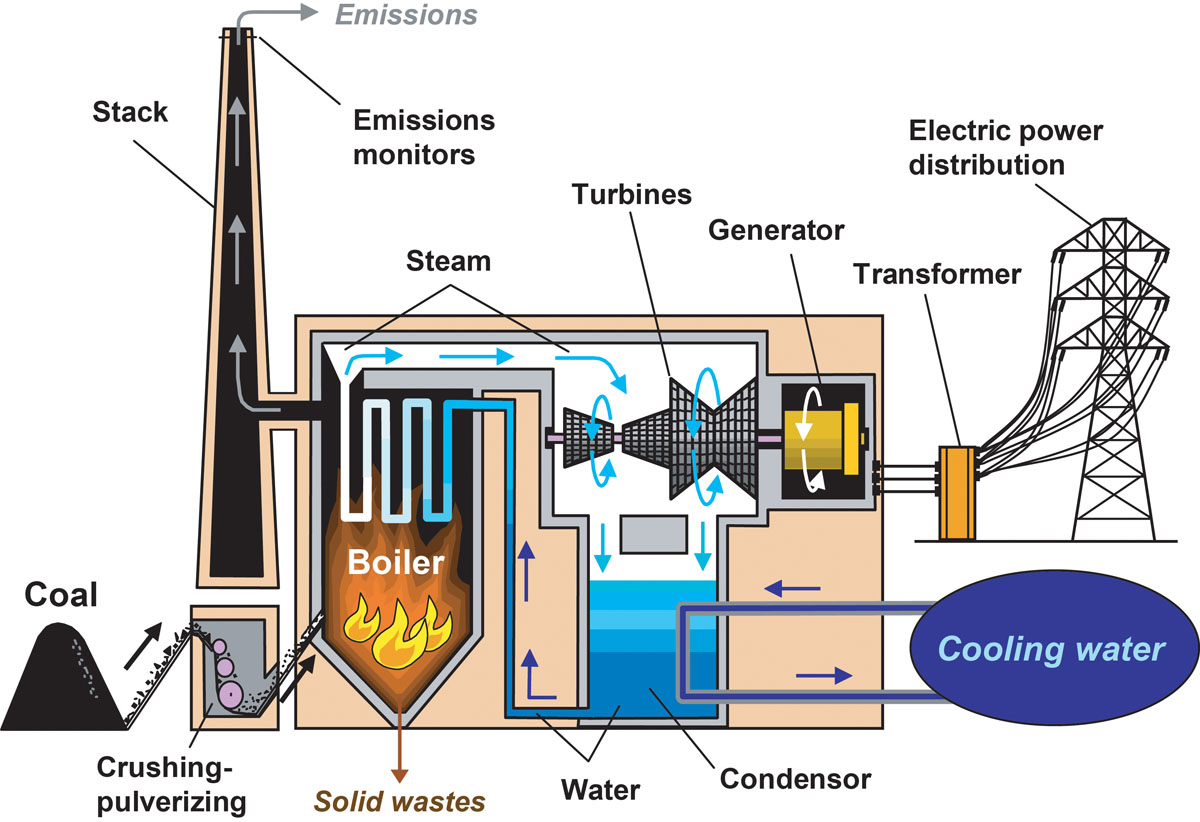
Coal is a brownish-black sedimentary rock that can be burned for fuel and used to generate electricity. It is composed mostly of carbon and hydrocarbons. Coal is the largest source of energy for generating electricity in the world, and the most abundant fossil fuel in the United States. Because coal takes millions of years to develop and there is a limited amount of it, it is a nonrenewable resource. Conditions that would eventually create coal began to develop about 300 million years ago, during the Carboniferous period. Anthracite contains 86%_97% carbon and generally has the highest heating value of all ranks of coal. Anthracite accounted for less than 1% of the coal mined in the United States in 2021. All of the anthracite mines in the United States are in northeastern Pennsylvania. It is mainly used by the metals industry. Bituminous coal contains 45%_86% carbon. Bituminous coal in the United States is between 100 million and 300 million years old. It is the most abundant rank of coal found in the United States, and it accounted for about 45% of total American coal production in 2021. Bituminous coal is used to generate electricity and is an important fuel and raw material for making coking coal or use in the iron and steel industry. Sub-bituminous coal typically contains 35%_45% carbon, and it has a lower heating value than bituminous coal. Most sub-bituminous coal in the United States is at least 100 million years old. About 46% of total American coal production in 2021 was subbituminous. Lignite contains 25%_35% carbon and has the lowest energy content of all coal ranks. Lignite coal deposits tend to be relatively young and were not subjected to extreme heat or pressure. It is crumbly and has high moisture content, which contributes to its low heating value. Lignite accounted for 8% of total American coal production in 2021. Lignite is mostly used to generate electricity. A facility in North Dakota also converts lignite to synthetic natural gas that is sent in natural gas pipelines to consumers in the East Coast. Peat is NOT coal, but can eventually transform into coal under the right circumstances. Peat is an accumulation of partly decayed vegetation that has gone through a small amount of carbonization. Peat contains energy that its original plants contained. It also contains high amounts of volatile matter and gases such as methane and mercury, which are environmentally hazardous when burned. Peat retains enough moisture to be spongy. It can absorb water and expand the bog to form more peat, which makes it a valuable environmental defense against flooding. It can also be integrated into soil to help it retain and slowly release water and nutrients. Hence, peat is valuable to gardeners. Peat is an important source of energy in many countries, including Ireland, Scotland, and Finland, where it is dehydrated and burned for heat. Click Here For Source
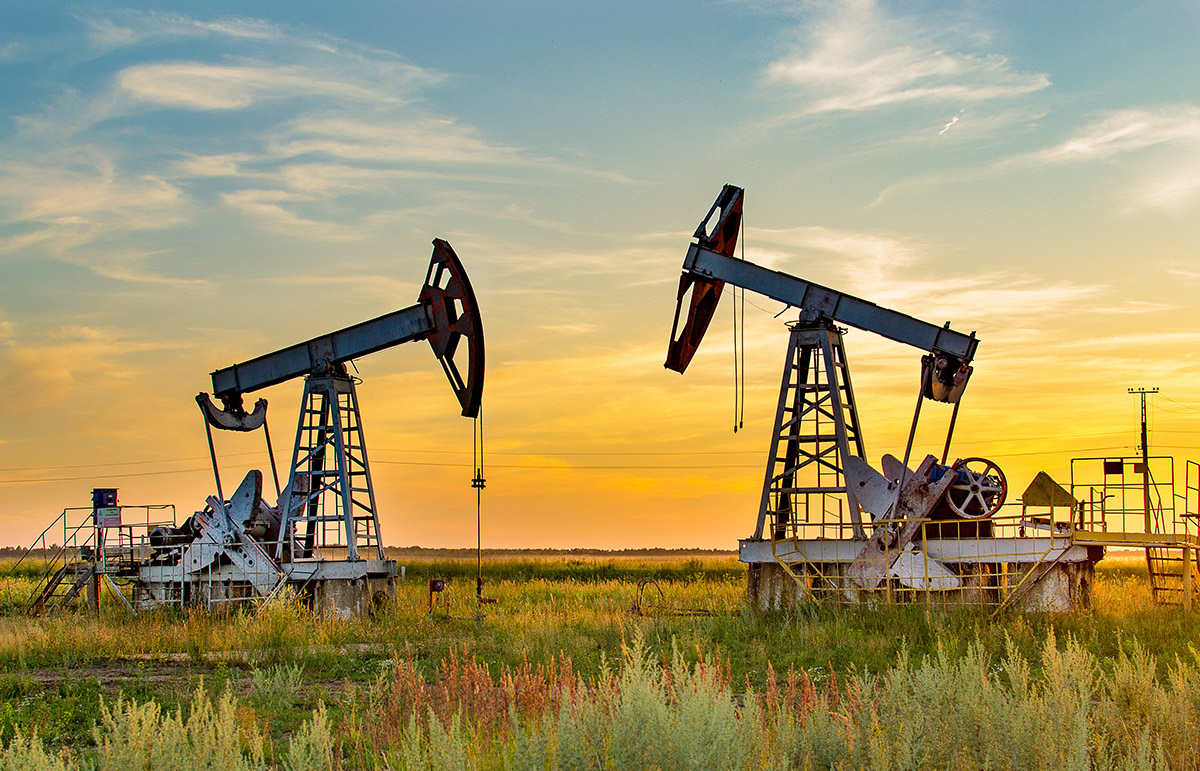
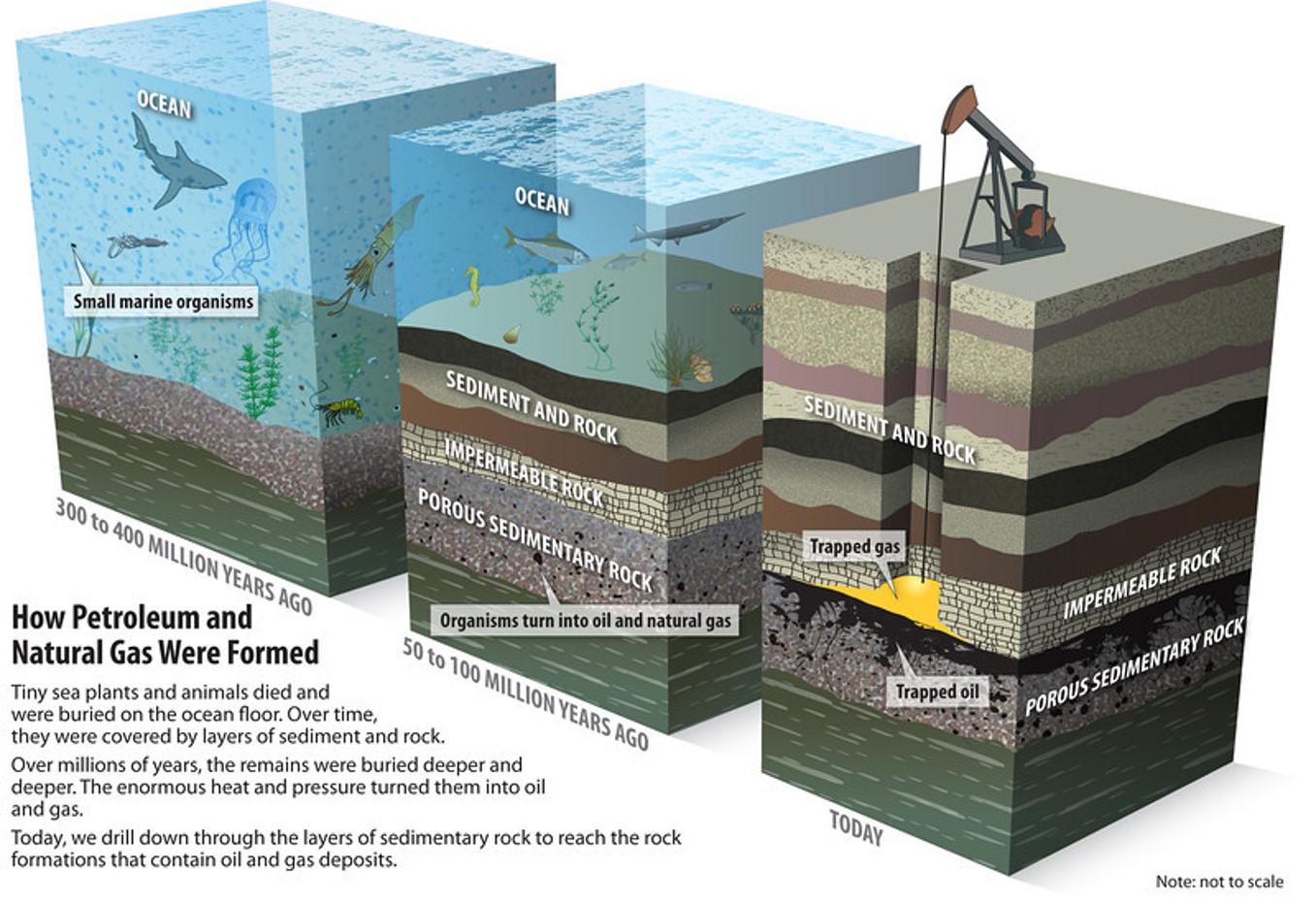
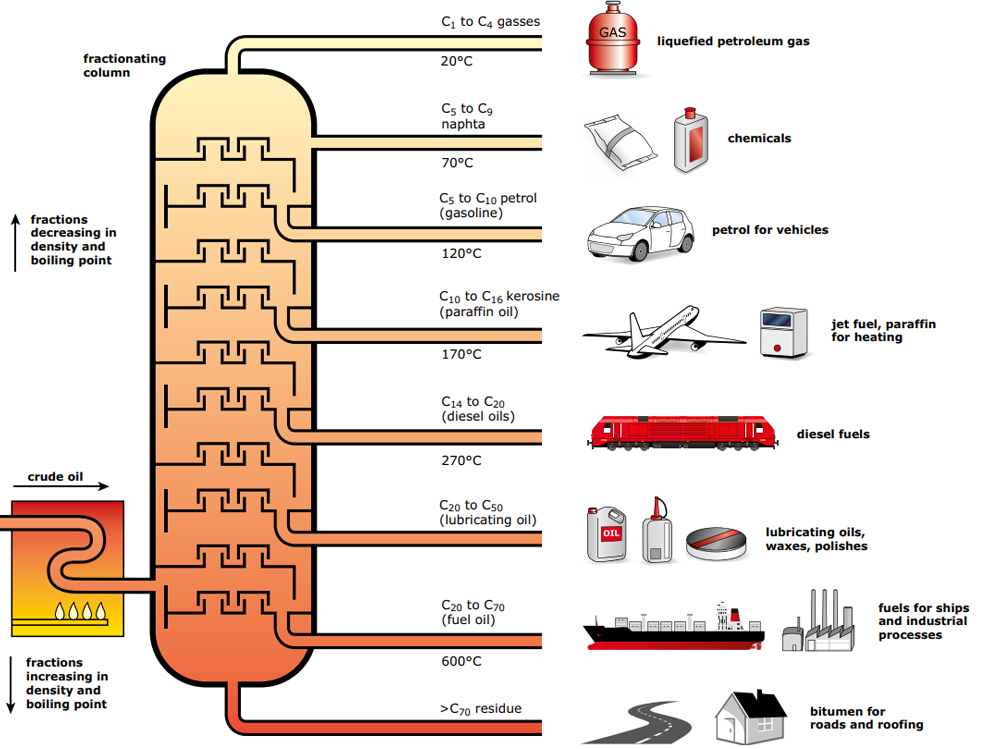
Petroleum is a mixture of hydrocarbons, water, and sulfur that occurs in underground deposits. It is found in vast underground reservoirs where ancient seas were located. Petroleum reservoirs, typically inside sedimentary rock layers, can be found beneath land or the ocean floor. Humans have been using oil for 7000 years. In the mid 1800s, the first modern oil well was drilled in Russia. Crude oil is usually black or dark brown, but can also be yellowish, reddish, tan, or even greenish. Color Variations indicate the distinct chemical composition of different samples of crude oil. Like coal, petroleum is a nonrenewable source of energy. It took millions of years for it to form, and when it is extracted and consumed, there is no way to replace it. Oil supplies is running out. Eventually, the world will reach peak oil, or its highest production level. Some experts predict peak oil could come as soon as 2050. Combusting gasoline, which is made from petroleum, is particularly harmful to the environment. Every 3.8 liters of pure gas that is combusted in a car engine releases about nine kilograms of carbon dioxide into the environment. When oil accidentally spills into the ocean, it can cause severe problems. Oil spills kill sea creatures, ruin a day at the beach, and make seafood unsafe to eat. It takes sound science to clean up the oil, measure the impacts of pollution, and help the ocean recover. Click Here For Source
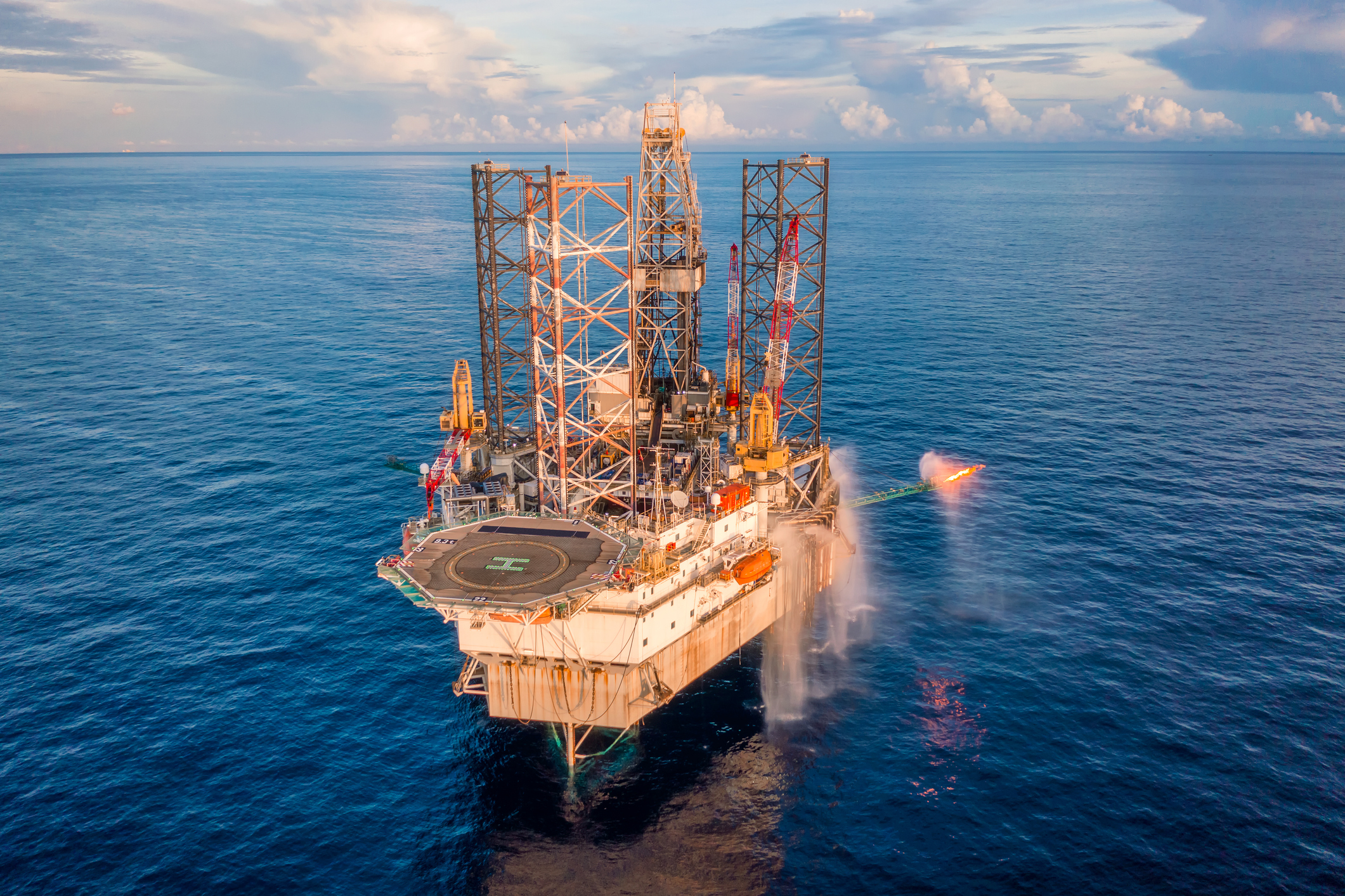
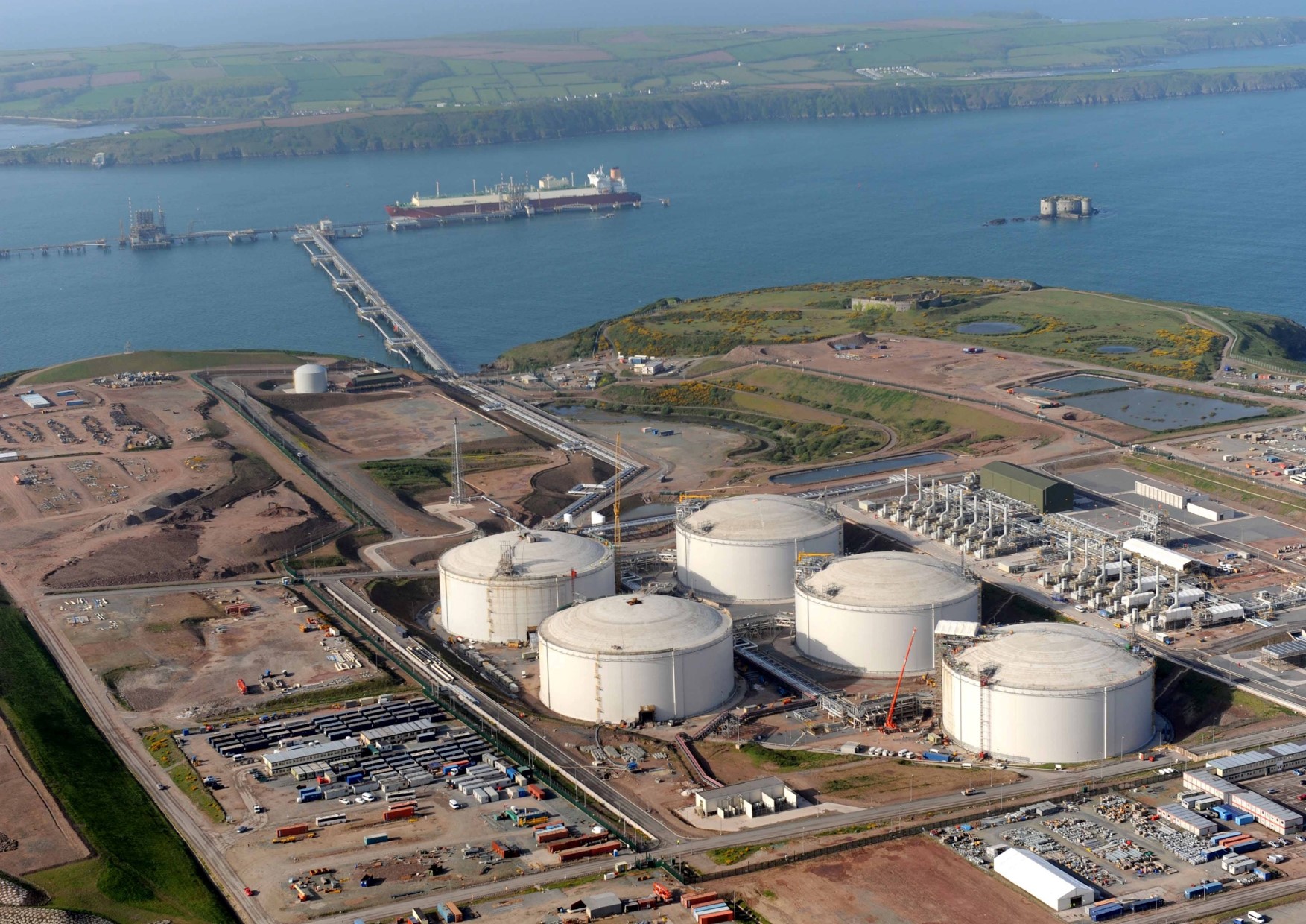
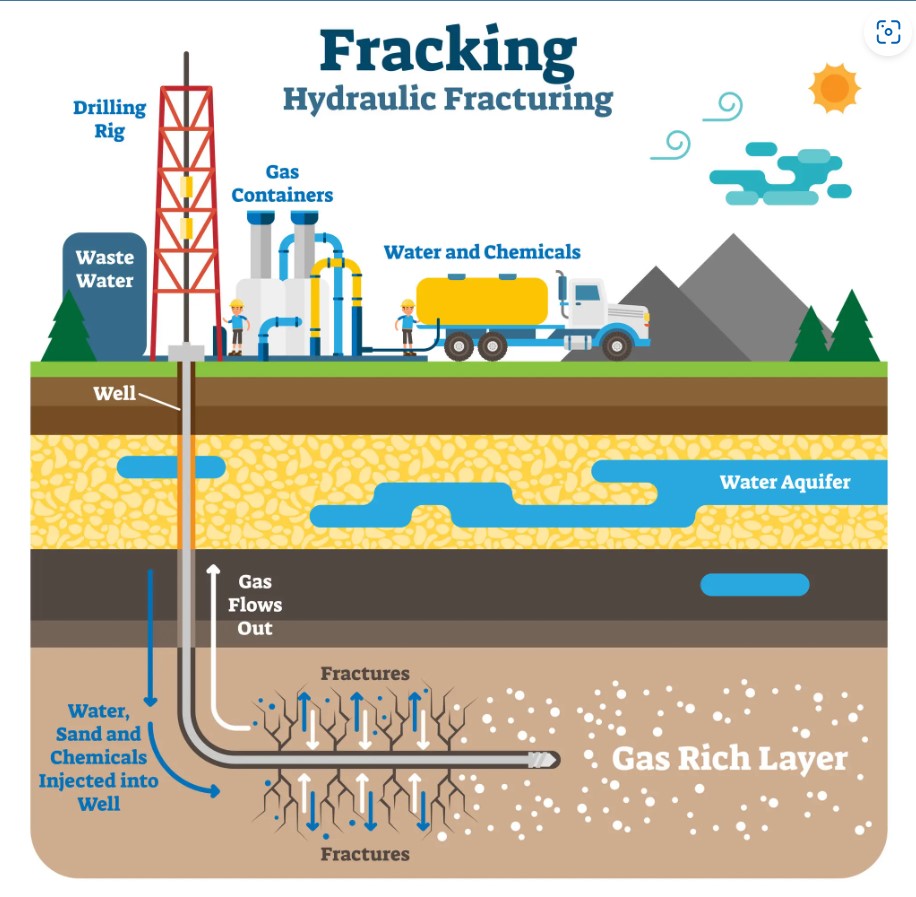
Like coal and petroleum, natural gas forms from the plants, animals, and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago. Natural gas deposits are often found near oil deposits. Deposits of natural gas close to Earth surface are usually dwarfed by nearby oil deposits. Deeper deposits have more natural gas than oil. The deepest deposits can be made up of pure natural gas. Today, natural gas is used in countless ways for industrial, commercial, residential, and transportation purposes. The United States Department of Energy estimates that natural gas can be up to 68 percent less expensive than electricity. Click Here For Source
Situation Of Distribution
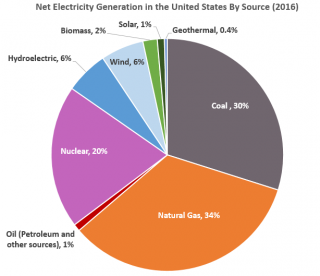
Natural gas provides the most electricity in US.
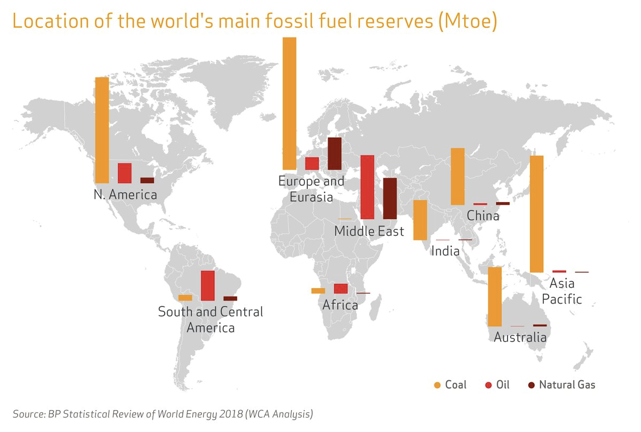
It is evident that the location of major coal reserve is different from that of major petroleum(natural gas) reserve.